Describe Prices and Output in a Perfectly Competitive Market
So the equilibrium will be set graphically at a three-way. A higher price and produce a larger output than a competitive firm.
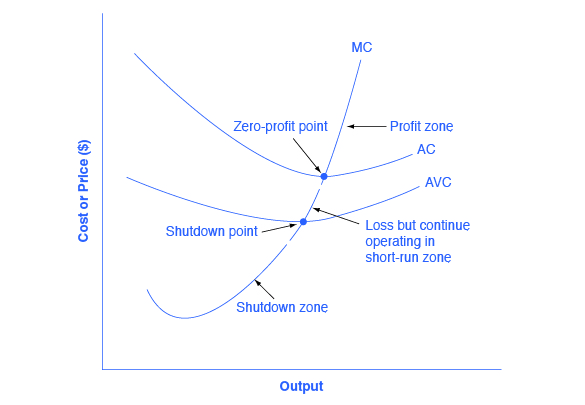
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions Principles Of Economics
The second factor labor is assumed to be freely and costlessly mobile between the two industries.
. Individual companies simply take the price determined by the market and produce that quantity of output that maximizes the companys profits. In other words not one single. One of the two factors of production typically capital is assumed to be specific to a particular industrythat is it is completely immobile.
The price elasticity of demand for Nanay Flors Photography is 05. The SF model assumes that an economy produces two goods using two factors of production capital and labor in a perfectly competitive market. The following figures describe the relevant costs of production.
The price is set by the interaction of demand and supply at the market or aggregate level. Since a perfectly competitive firm is so small relative to the market that however much output it supplies will have no effect on the market price it can sell all it wants at the going market price. Ease of Entry and Exit The assumption that it is easy for other firms to enter a perfectly competitive market implies an even greater degree of competition.
If for whatever reason in the short run output is above potential output over time as prices. The marginal revenue product of labor MRP L is the marginal product of labor MP L times the marginal revenue which is the same as price under perfect competition the firm obtains from additional units of output that result from hiring the additional unit of laborIf an additional worker adds 4 units of output per day to a firms production and if each of those 4 units sells for 20. Example of Optimal Price and Output in Perfectly Competitive Markets.
A competitive market is one where there are numerous producers that compete with one another in hopes to provide goods and services we as consumers want and need. Different prices for the same product in a certain market. Many many firms produce in a monopolistically competitive industry.
A lower price and produce a smaller output than a competitive firm. Similarly in some circumstances. Please briefly describe the main ideas and differences between these models.
In perfect competition any profit-maximizing producer has a market price equal to its marginal cost PMC. Buyers though not necessarily sellers perceive differences in the products of several. In a perfectly competitive market long-run equilibrium will occur when the marginal costs of production equal the average costs of production which also equals marginal revenue from selling the goods.
All companies of a PC market are price takers. In a perfectly competitive market in the long-term this is taken one step further. Features that make one product appear different from competing products in the same market.
The selling of identical products in different markets. The following are some of the main assumptions of the model. A higher price and produce a smaller output than a competitive firm.
Market power to a seller is the ability profitably to maintain prices above competitive levels for a significant period of time. In an economy a perfectly competitive market is the place where anyone is allowed to enter or exit question_answer Q. The same price and produce the same output as a competitive firm.
The profit is maximized when. This assumption is similar to that found in a model of perfect competition. Question 1 In the market for swim suits demand is P 58 - 0011Q and supply is P 5 0009Q.
In a free market the laws and forces of supply and demand are free from any intervention by a government or other authority other than those interventions which are made to prohibit market coercions. Perfectly competitive PC companies have zero market power when it comes to setting prices. 6 In some circumstances a sole seller a monopolist of a product with no good substitutes can maintain a selling price that is above the level that would prevail if the market were competitive.
The charging of different prices for the same product in different markets. A firm uses a single input to produce its output which is sold in a. The curve that depicts quantities of goods being demanded by individuals at various levels of price question_answer.
If the price function P 20 Q and MC 5 2Q calculate the profit-maximizing price and output. A monopolistically competitive market has features that represent a cross between a perfectly competitive market and a monopolistic market hence the name. In economics a free market is a system in which the prices for goods and services are self-regulated by buyers and sellers negotiating in an open market without market coercions.
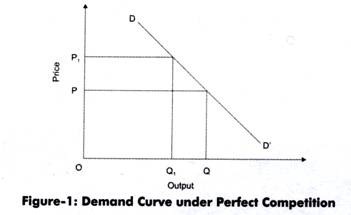
A firm in a perfectly competitive market can react to prices but cannot affect the prices it pays for the factors of production or the prices it receives for its output. In short a perfectly competitive firm faces a horizontal demand curve at the market price.
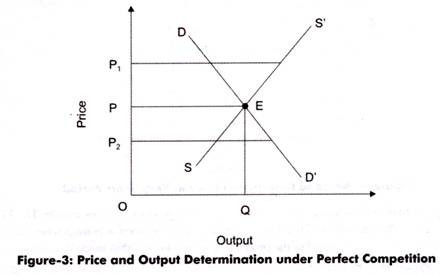
Price And Output Determination Under Perfect Competition

Reading Price And Revenue In A Perfectly Competitive Industry And Firm Microeconomics

Price And Output Determination Under Perfect Competition
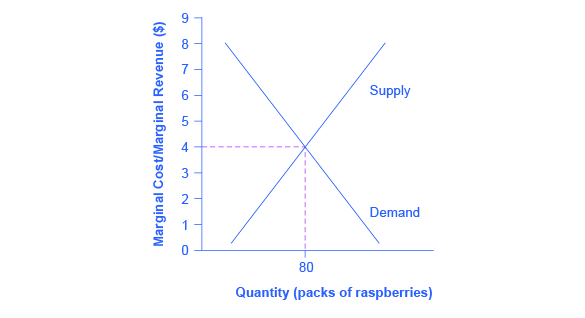
8 2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions Principles Of Economics
No comments for "Describe Prices and Output in a Perfectly Competitive Market"
Post a Comment